Aligning a structure to another
We use align.alignto to align a structure to another.
Last updated: December 2022
Minimum version of MDAnalysis: 1.0.0
Packages required:
Optional packages for molecular visualisation:
Throughout this tutorial we will include cells for visualising Universes with the NGLView library. However, these will be commented out, and we will show the expected images generated instead of the interactive widgets.
See also
Note
MDAnalysis implements RMSD calculation using the fast QCP algorithm ([The05]) and a rotation matrix R that minimises the RMSD ([LAT09]). Please cite ([The05]) and ([LAT09]) when using the MDAnalysis.analysis.align module in published work.
[1]:
import MDAnalysis as mda
from MDAnalysis.analysis import align
from MDAnalysis.tests.datafiles import CRD, PSF, DCD, DCD2
# import nglview as nv
import warnings
# suppress some MDAnalysis warnings about writing PDB files
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
Loading files
The test files we will be working with here are trajectories of a adenylate kinase (AdK), a phosophotransferase enzyme. ([BDPW09]) The trajectories sample a transition from a closed to an open conformation.
[2]:
adk_open = mda.Universe(CRD, DCD2)
adk_closed = mda.Universe(PSF, DCD)
[3]:
# adk_open_view = nv.show_mdanalysis(adk_open)
# adk_open_view
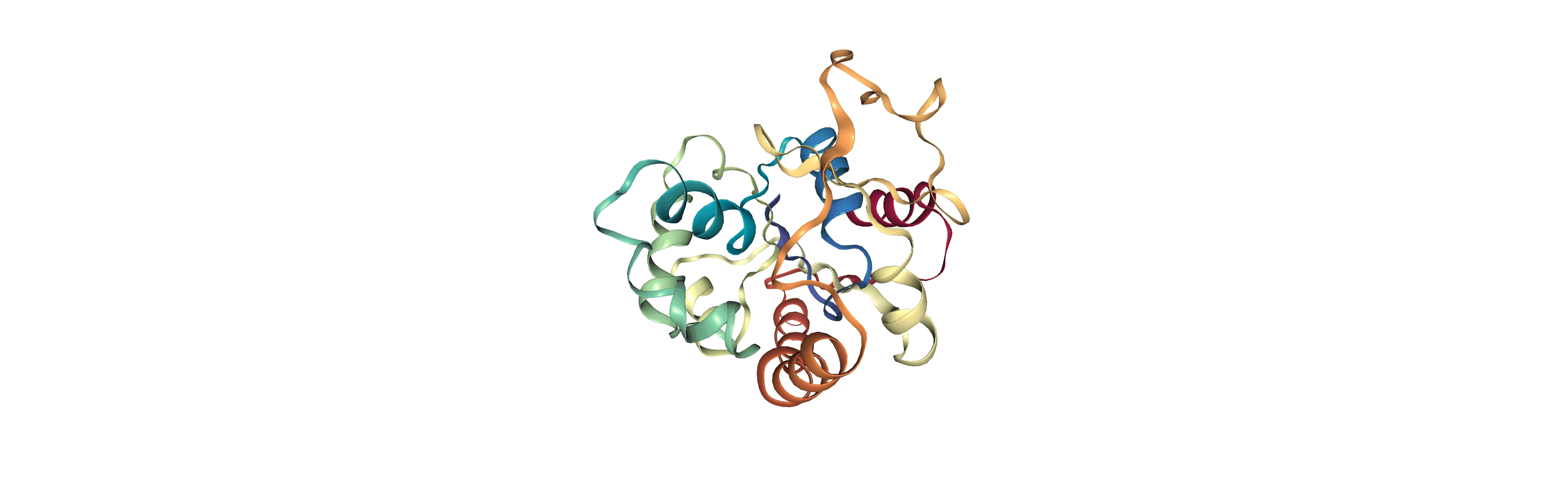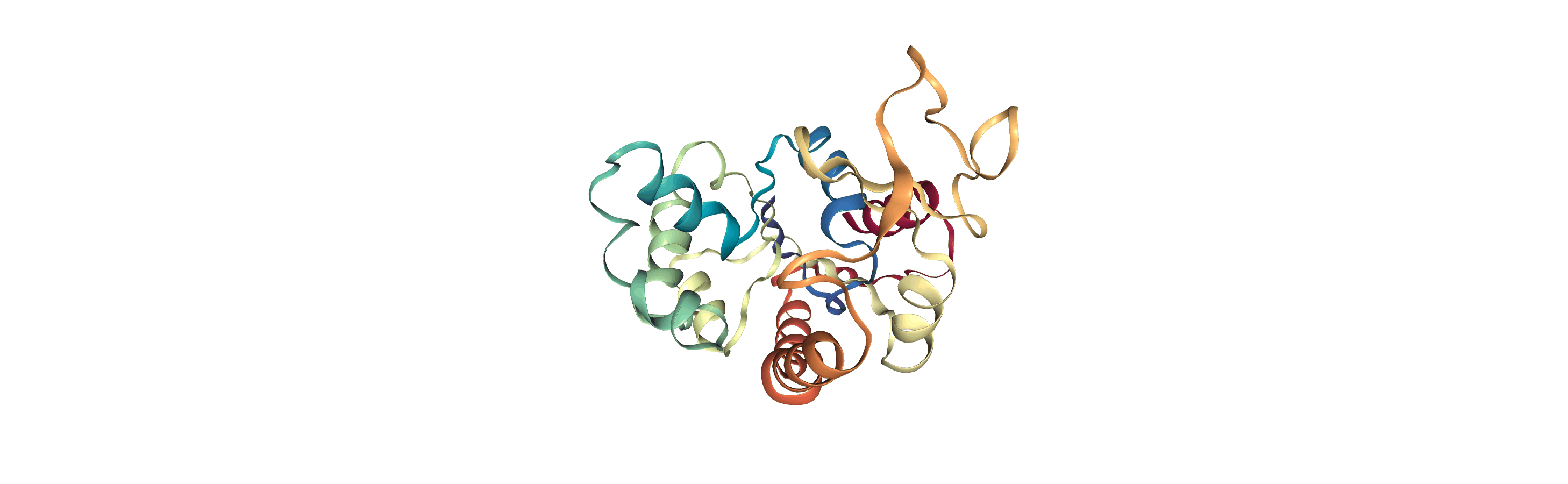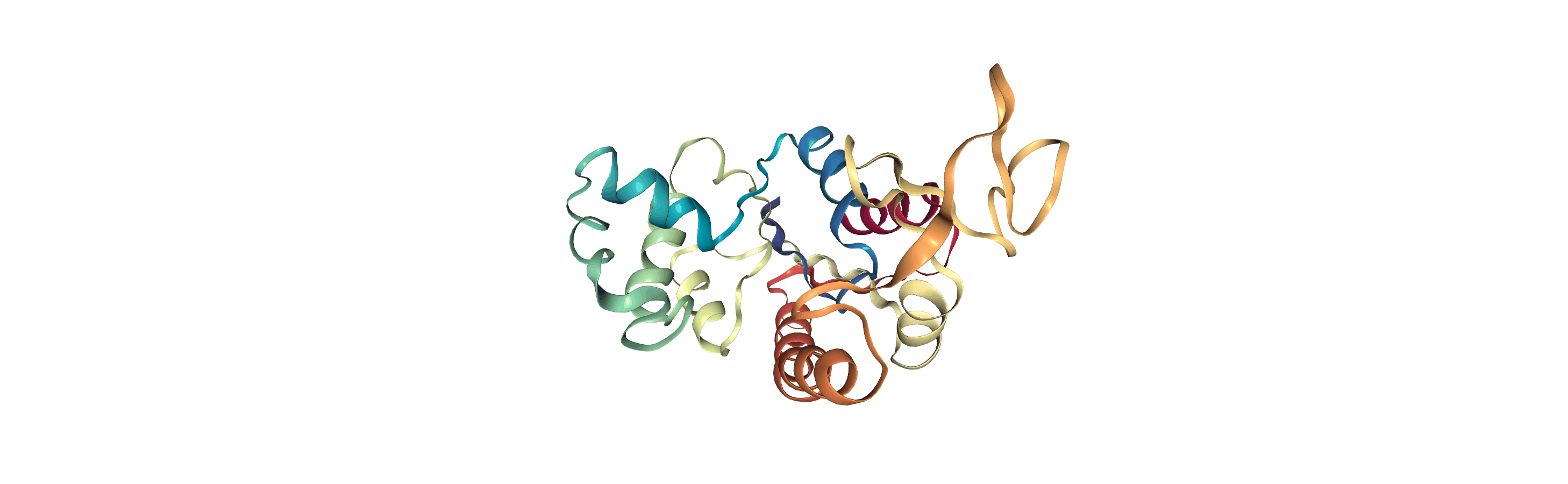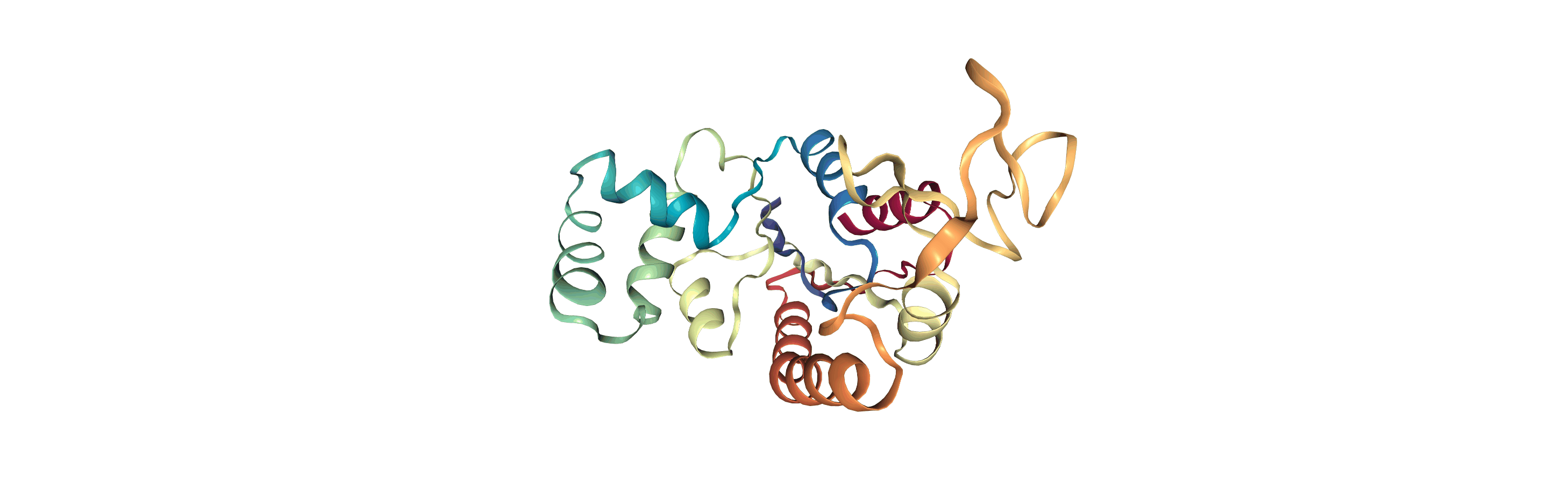
[4]:
# adk_closed_view = nv.show_mdanalysis(adk_closed)
# adk_closed_view
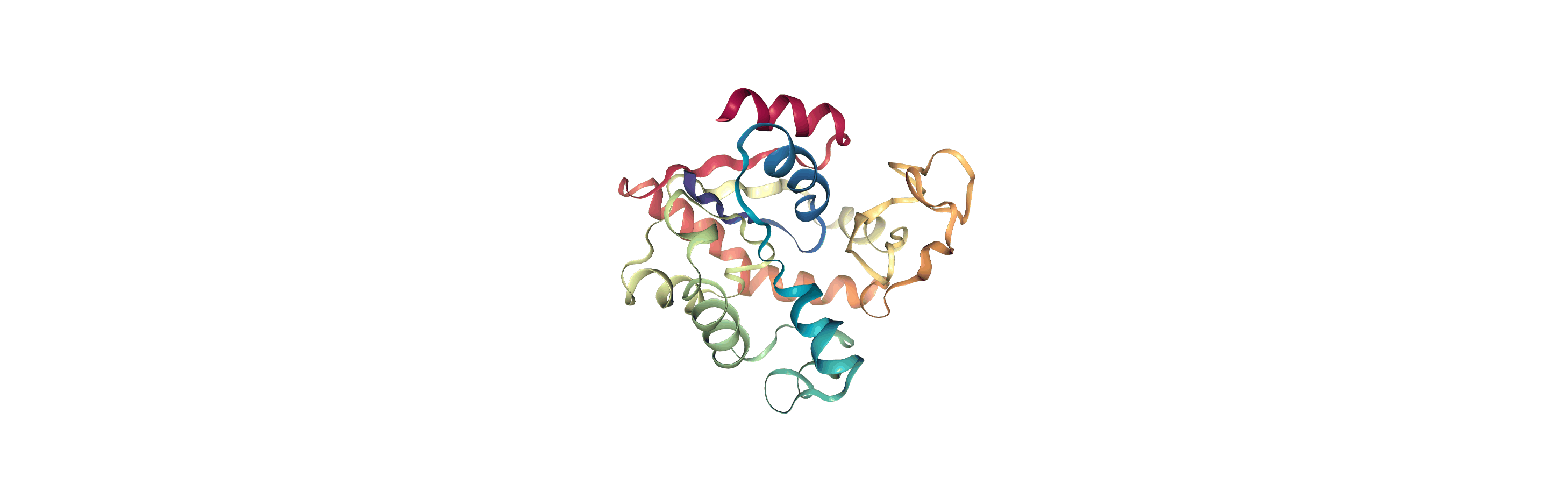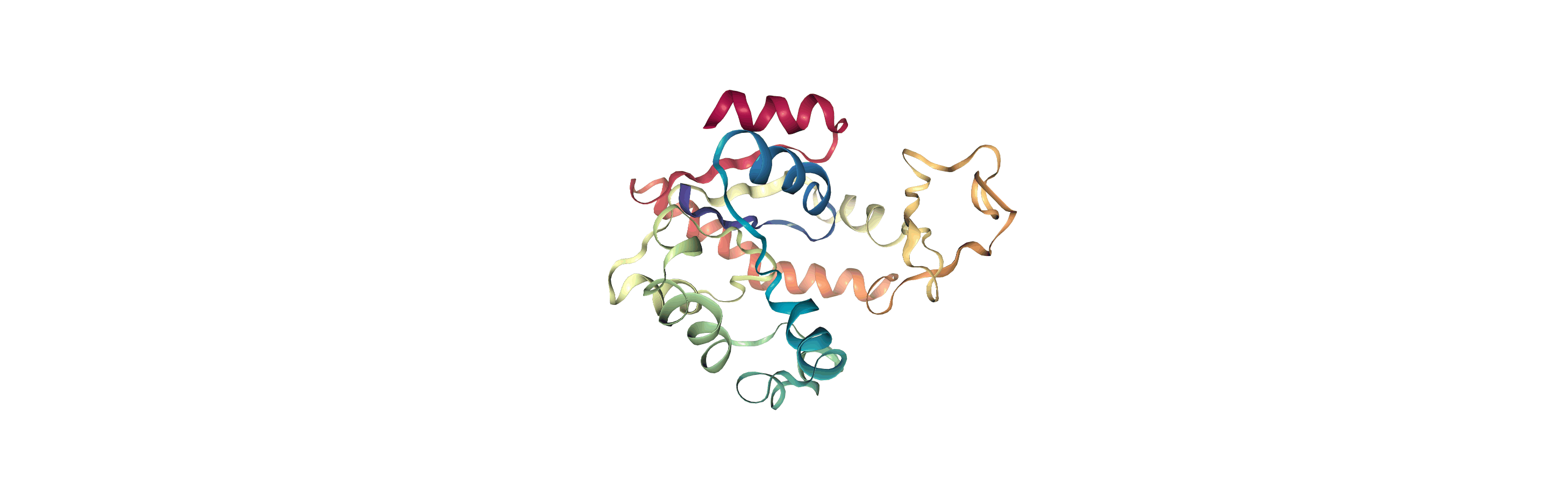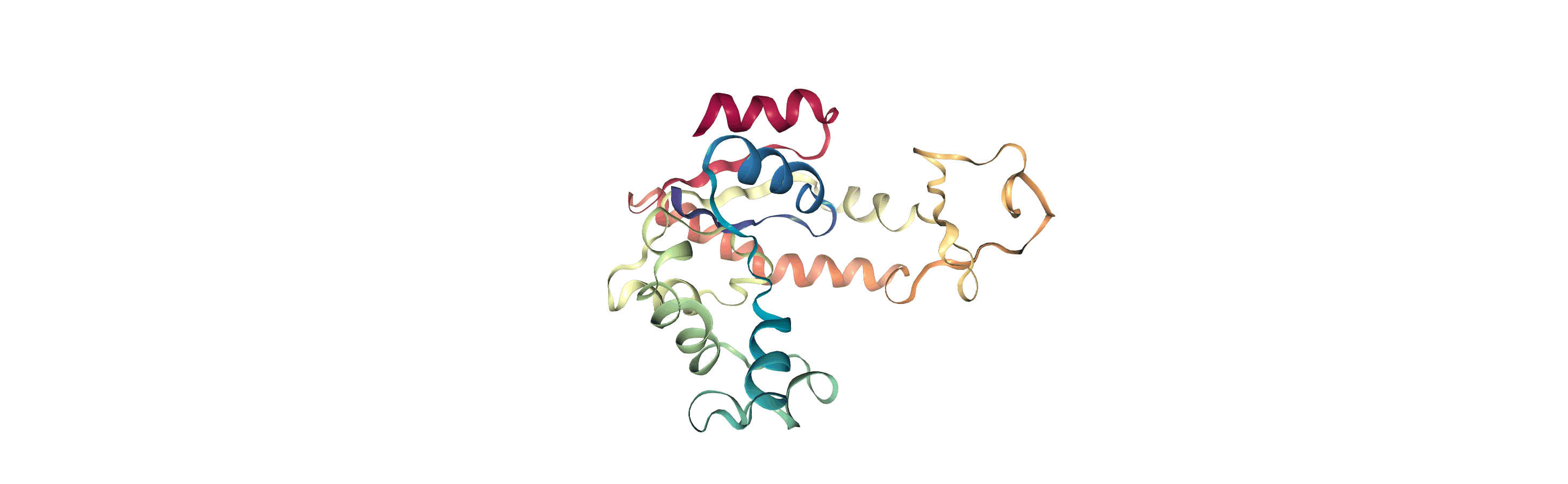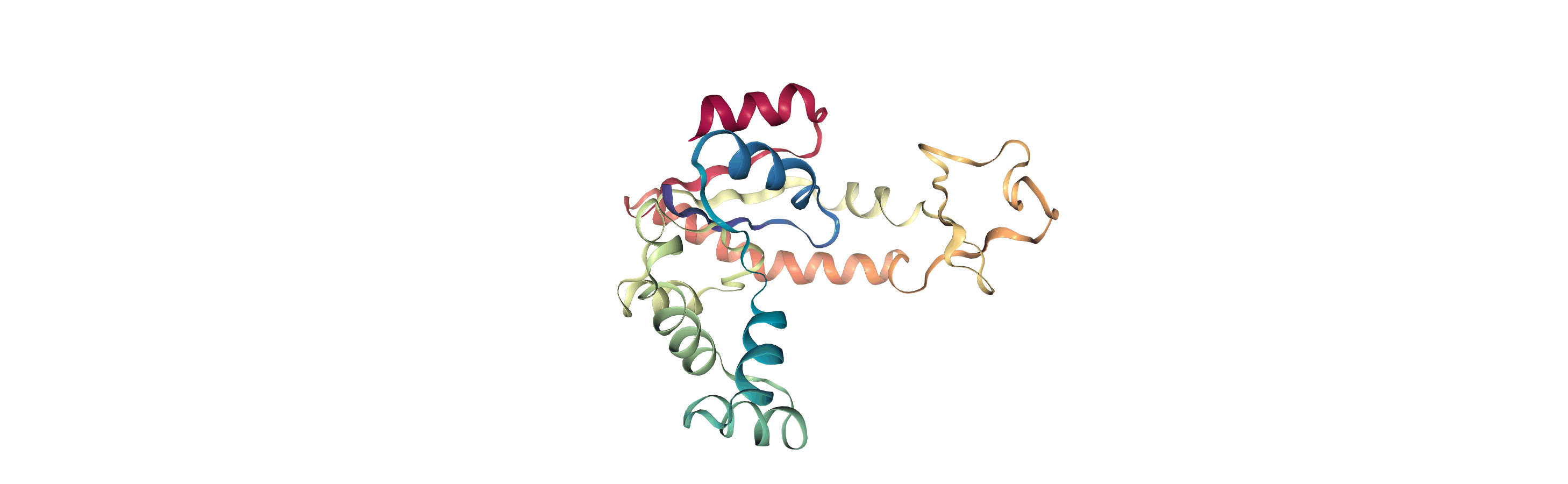
Currently, the proteins are not aligned to each other. The difference becomes even more obvious when the closed conformation is compared to the open. Below, we set adk_open to the last frame and see the relative positions of each protein in a merged Universe.
[5]:
adk_open.trajectory[-1] # last frame
merged = mda.Merge(adk_open.atoms, adk_closed.atoms)
[6]:
# merged_view = nv.show_mdanalysis(merged)
# merged_view
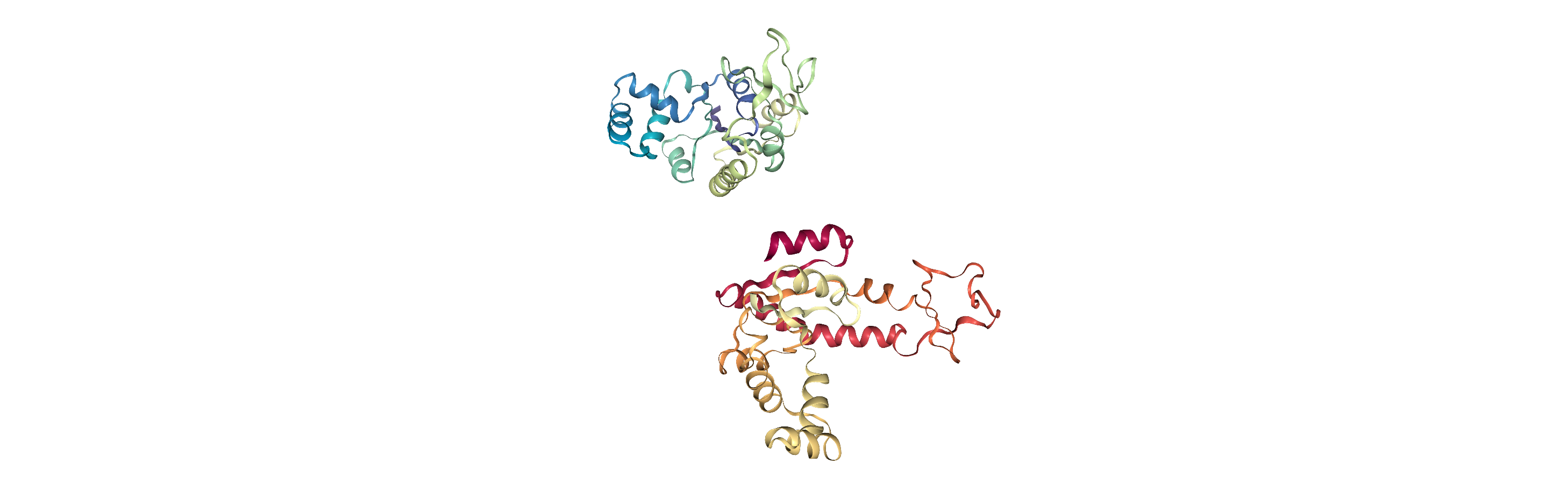
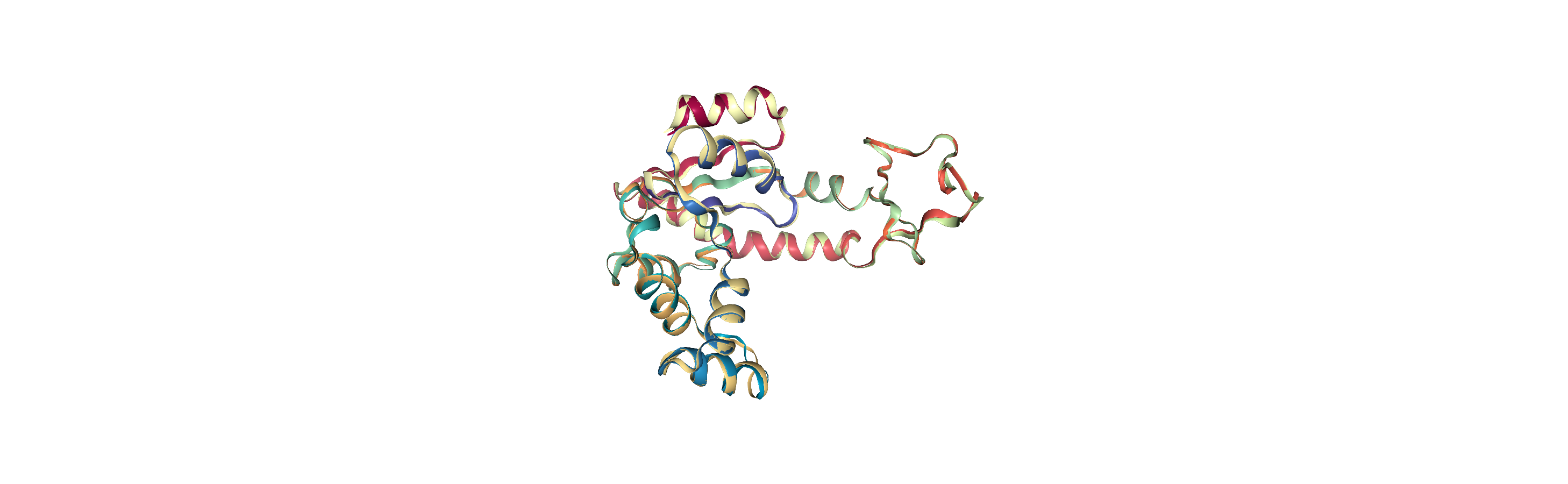
Aligning a structure with align.alignto
alignto (API docs) aligns the mobile AtomGroup to the target AtomGroup by minimising the root mean square deviation (RMSD) between particle positions (please see the linked notebook for an explanation of RMSD). It returns (old_rmsd, new_rmsd). By default (match_atoms=True), it will attempt to match the atoms between the mobile and reference structures by
mass.
[7]:
rmsds = align.alignto(adk_open, # mobile
adk_closed, # reference
select='name CA', # selection to operate on
match_atoms=True) # whether to match atoms
print(rmsds)
(np.float64(21.712154435976014), 6.817293751703919)
[8]:
# aligned_view = nv.show_mdanalysis(mda.Merge(adk_open.atoms, adk_closed.atoms))
# aligned_view
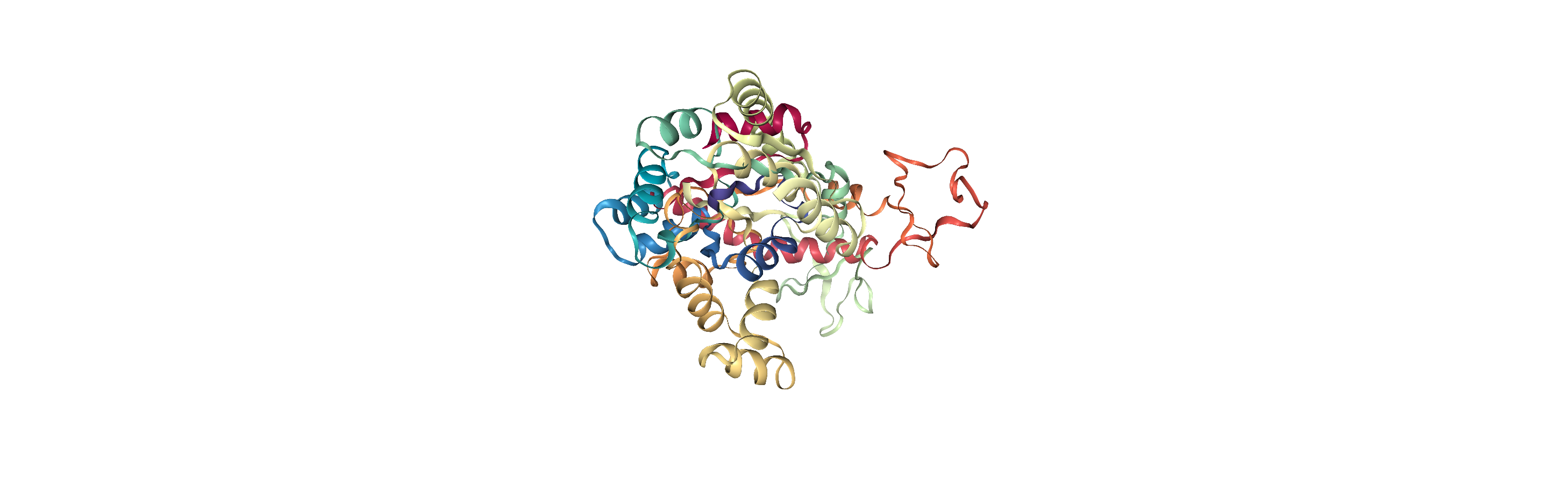
However, you may want to align to a structure that where there is not a clear match in particle mass. For example, you could be aligning the alpha-carbons of an atomistic protein to the backbone beads of a coarse-grained structure. Below, we use the somewhat contrived example of aligning 214 alpha-carbons to the first 214 atoms of the reference structure. In this case, we need to switch match_atoms=False or the alignment will error.
[9]:
rmsds = align.alignto(adk_open.select_atoms('name CA'), # mobile
adk_closed.atoms[:214], # reference
select='all', # selection to operate on
match_atoms=False) # whether to match atoms
print(rmsds)
(np.float64(18.991465038265208), 16.603704620787127)
[10]:
# shifted_aligned_view = nv.show_mdanalysis(mda.Merge(adk_open.atoms, adk_closed.atoms))
# shifted_aligned_view
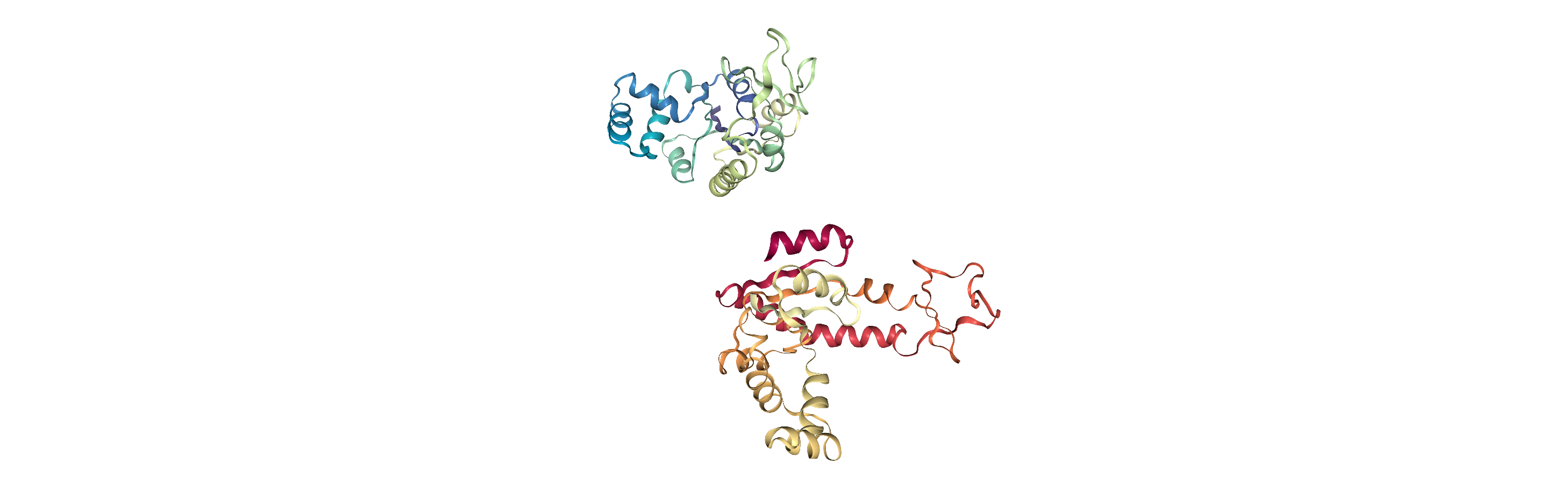
When we align structures, positions are set temporarily. If we flip to the first frame of adk_open and back to the last frame, we can see that it has returned to its original location.
[11]:
adk_open.trajectory[0] # set to first frame
adk_open.trajectory[-1] # set to last frame
[11]:
< Timestep 101 >
[12]:
# reset_view = nv.show_mdanalysis(mda.Merge(adk_open.atoms, adk_closed.atoms))
# reset_view
You can save the aligned positions by writing them out to a PDB file and creating a new Universe.
[13]:
align.alignto(adk_open, adk_closed, select='name CA')
adk_open.atoms.write('aligned.pdb')
[14]:
# from_file_view = nv.show_mdanalysis(mda.Universe('aligned.pdb'))
# from_file_view
References
[1] Oliver Beckstein, Elizabeth J. Denning, Juan R. Perilla, and Thomas B. Woolf. Zipping and Unzipping of Adenylate Kinase: Atomistic Insights into the Ensemble of Open↔Closed Transitions. Journal of Molecular Biology, 394(1):160–176, November 2009.
URL: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0022283609011164, doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2009.09.009.
[2] Richard J. Gowers, Max Linke, Jonathan Barnoud, Tyler J. E. Reddy, Manuel N. Melo, Sean L. Seyler, Jan Domański, David L. Dotson, Sébastien Buchoux, Ian M. Kenney, and Oliver Beckstein. MDAnalysis: A Python Package for the Rapid Analysis of Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Proceedings of the 15th Python in Science Conference, pages 98–105, 2016.
URL: https://conference.scipy.org/proceedings/scipy2016/oliver_beckstein.html, doi:10.25080/Majora-629e541a-00e.
[3] Pu Liu, Dimitris K. Agrafiotis, and Douglas L. Theobald. Fast determination of the optimal rotational matrix for macromolecular superpositions. Journal of Computational Chemistry, pages n/a–n/a, 2009. URL: http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/jcc.21439, doi:10.1002/jcc.21439.
[4] Naveen Michaud-Agrawal, Elizabeth J. Denning, Thomas B. Woolf, and Oliver Beckstein. MDAnalysis: A toolkit for the analysis of molecular dynamics simulations. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 32(10):2319–2327, July 2011.
URL: http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/jcc.21787, doi:10.1002/jcc.21787.
[5] Hai Nguyen, David A Case, and Alexander S Rose. NGLview–interactive molecular graphics for Jupyter notebooks. Bioinformatics, 34(7):1241–1242, April 2018.
URL: https://academic.oup.com/bioinformatics/article/34/7/1241/4721781, doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btx789.
[6] Douglas L. Theobald. Rapid calculation of RMSDs using a quaternion-based characteristic polynomial. Acta Crystallographica Section A Foundations of Crystallography, 61(4):478–480, July 2005.
URL: http://scripts.iucr.org/cgi-bin/paper?S0108767305015266, doi:10.1107/S0108767305015266.